The Hidden Cost of ‘Direct’ Traffic: Ad Blockers/Antivirus Steal Credit From Your Best Marketing Channels
Executive Summary
Research shows approximately 30% of traffic labeled as “direct” in Google Analytics 4 actually originates from other marketing channels – with organic search suffering the most severe misattribution at roughly 60%.
Business Impact: If your analytics show $100,000 in monthly revenue from “direct” traffic, approximately $30,000 likely comes from other sources – with $18,000 (60%) originating from organic search, $9,000 (30%) from social media, and $3,000 (10%) from paid advertising and email combined.
The Solution: Understanding these attribution patterns allows businesses to make better budget allocation decisions. This article explains which channels lose the most attribution credit, why organic search traffic gets systematically underreported, and practical steps to improve tracking accuracy.
Understanding Direct Traffic Misattribution in Google Analytics 4
Most businesses unknowingly undervalue their best-performing marketing channels. Research shows approximately 30% of traffic labeled as “direct” in Google Analytics 4 actually originates from other sources – with organic search being the most severely affected. When roughly 60% of misattributed traffic comes from search engines, businesses risk cutting SEO budgets precisely when they should invest more.
Business owners invest thousands of dollars monthly in marketing campaigns, carefully tracking results to identify winning strategies. Yet privacy tools systematically distort this data. With approximately 32% of Americans using ad blockers, combined with privacy features in Brave browser’s tracking prevention, Firefox’s Enhanced Tracking Protection, and Apple’s Safari Intelligent Tracking Prevention, these privacy tools affect attribution across all major marketing channels.
The problem stems from three critical tracking mechanisms failing: UTM parameters get stripped from URLs, referrer headers get blocked or truncated, and tracking cookies get deleted or capped. These failures funnel marketing-driven traffic into Google Analytics 4’s catch-all “(direct)/(none)” bucket. GA4’s attribution models exclude direct visits entirely unless the entire customer journey consists solely of direct sessions, causing paid campaigns to lose conversion credit when the final visit gets misclassified as “direct.”
Breaking Down Misattributed “Direct” Traffic: Where It Really Comes From
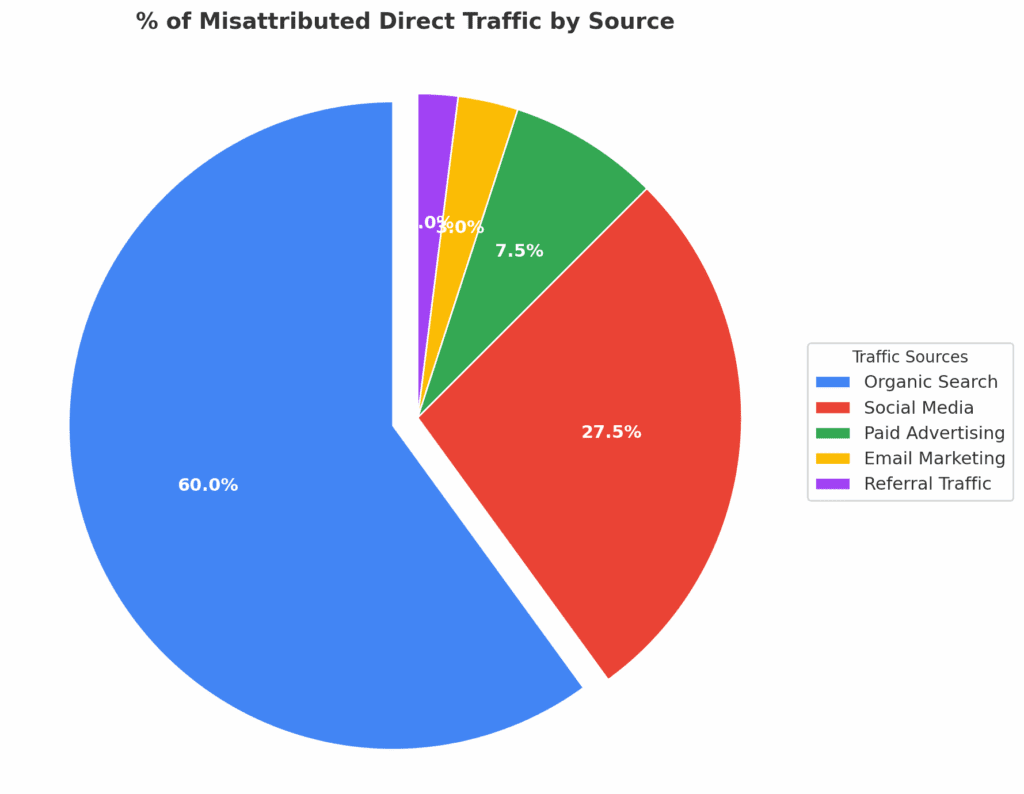
Breaking Down Misattributed “Direct” Traffic: Where It Really Comes From
Misattribution does not affect all marketing channels equally. Some channels lose far more attribution credit than others based on their technical tracking mechanisms. Research shows 30% of direct traffic originates elsewhere, but this misattributed traffic disproportionately originates from specific channels.
| Channel Type | Share of Misattributed Traffic Within “Direct” | Why This Channel Gets Hidden in “Direct” | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🔍 Organic Search | ~60% of Misattributed Traffic (~18% of total “direct” if 30% is misattributed) |
Organic search relies 100% on referrer headers with zero UTM backup. Browsers strip or truncate these headers aggressively. Users rarely type long URLs but frequently find them via search engines. | Your SEO generates 50-70% more traffic than analytics shows. Budget decisions based on reported organic search traffic systematically underfund your highest-intent channel. |
| 📱 Social Media | ~25-30% of Misattributed Traffic (~8-9% of total “direct”) |
Private sharing (WhatsApp, Messenger, Slack) passes 0% attribution. Public platforms pass accurate data only 12-30% of the time. High mobile usage increases Safari ITP impact. | 70-88% of social traffic gets misattributed. Social media ROI calculations significantly underestimate true performance, especially for viral content shared privately. |
| 💰 Paid Advertising | ~10% of Misattributed Traffic (~3% of total “direct”) |
Protected by platform click IDs (gclid, fbclid) plus UTM parameters. However, iOS 17 strips click IDs in Messages/Mail/Private Browsing. Ad blockers can still remove UTMs. | Automated bidding algorithms receive incomplete signals. Platforms may incorrectly conclude campaigns underperform, automatically reducing bids or narrowing targeting. |
| 📧 Email Marketing | ~5% of Misattributed Traffic (~1% of total “direct”) |
Email campaigns can be fully UTM-tagged by marketers. Attribution fails only when recipients forward via messaging apps or antivirus software strips parameters before email opens. | Most accurately tracked channel. Proper UTM implementation maintains attribution for 90-95% of email-driven traffic. |
How to read this table: If you have 1,000 “direct” sessions, approximately 700 are genuinely direct, while ~180 actually originated from organic search, ~90 from social media, ~30 from paid ads, and ~20 from email/referrals. These percentages vary by industry and audience demographics but provide a research-backed framework for understanding attribution gaps.
Quick Audit: Is Misattribution Affecting Your Business?
5-Minute Diagnostic Checklist
☐ Step 1: Check your direct traffic percentage (2 minutes)
- Navigate to: GA4 → Reports → Acquisition → Traffic Acquisition
- Locate your “Direct” traffic percentage
- Healthy range: 10-25%
- Yellow flag: 26-35%
- Red flag: 36% or higher
☐ Step 2: Examine landing pages (2 minutes)
- Navigate to: GA4 → Reports → Engagement → Landing Pages
- Apply filter: “Direct” traffic only
- Red flags indicating misattribution:
- Blog posts appearing in top 10 landing pages
- Product pages with long, complex URLs
- Resource downloads or guides
- Any page users wouldn’t realistically type manually
☐ Step 3: Compare month-over-month trends (1 minute)
- Compare last month’s data to previous month
- Inverse correlation suggests attribution transfer:
- Direct traffic increasing by 150 sessions?
- Organic search decreasing by similar amount?
- This pattern indicates attribution shifting, not actual performance change
Interpretation Guide:
- If you identified 2+ red flags: You likely experience significant misattribution. Proceed to the Solutions section for remediation steps.
- If direct traffic exceeds 36%: Address this issue immediately – your strategic decisions rely on fundamentally distorted data.
- If direct traffic ranges 26-35%: Plan improvements this quarter to restore data integrity.
- If direct traffic stays below 25%: Monitor trends and maintain good tracking practices.
📊 Case Study: When Groupon Lost Google Rankings for 6 Hours
In 2014, Groupon was accidentally de-indexed from Google for six hours. Their “direct” traffic immediately dropped by 60%, revealing that the majority of what appeared as direct brand recognition actually represented organic search traffic being systematically misattributed.
The analysis specifically examined direct traffic to long, non-branded URLs – product detail pages that users discover through search engines but would never type manually. When the referrer headers that enable organic search attribution disappeared, these sessions defaulted to “direct” classification.
Why This Still Applies Today: While browser privacy protections have intensified since 2014, the fundamental tracking mechanism – referrer headers being stripped or truncated – remains identical. If anything, the proliferation of privacy-focused browsers (Brave, DuckDuckGo), stricter default browser settings, and iOS tracking prevention suggest the 60% figure now represents a conservative estimate.
A follow-up analysis by Conductor applied Groupon’s findings to broader industry data. By reallocating 60% of direct traffic to organic search, they calculated that organic’s true share increased from 47% to 64% of total website traffic across their dataset.
How Privacy Tools Break Marketing Attribution
Google Analytics 4 assigns traffic to the “(direct)/(none)” channel when sessions lack identifiable referral sources or campaign tags. In an ideal scenario, direct traffic represents users who genuinely know your brand and navigate to your website by typing the URL directly, clicking a saved bookmark, or following a link from an offline document like a PDF.
For most healthy websites, direct traffic typically represents 10-25% of sessions. When this percentage climbs above 30%, it signals a problem: your analytics platform cannot identify visitor origins.
The Three Ways Tracking Mechanisms Fail
1. Ad Blockers Strip UTM Parameters: UTM parameters serve as the foundation of campaign tracking. These text snippets append to URLs to tell GA4 exactly which campaign, source, and medium drove each visit. A newsletter link might look like: yoursite.com/?utm_source=newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=spring_sale.
Modern ad blockers systematically dismantle this tracking. Extensions like uBlock Origin strip parameters from URLs before pages load. AdGuard’s URL Tracking filter removes UTM codes. The technical process happens invisibly: a user clicks your carefully tagged email link, their ad blocker intercepts the request, strips the UTM parameters, and the clean URL reaches your website. GA4 sees a visitor arriving with no source information and defaults to classifying the session as “direct.”
2. Browsers Block Referrer Headers: The HTTP Referer header contains originating URLs. When someone clicks a link from Facebook to your website, their browser sends a request that includes “facebook.com” in the referrer field, allowing GA4 to classify the traffic as social media referral. This native web mechanism provides automatic source attribution without requiring manual UTM tagging.
Modern browsers systematically limit this data flow. Most browsers default to strict-origin-when-cross-origin policy, which trims cross-origin referrers to show only the domain origin rather than the complete URL with path information. Privacy-focused browsers implement even stricter policies: Brave removes known tracking parameters automatically, while Firefox strips advertising tracking parameters by default.
3. Safari Caps Cookies at Seven Days: Apple’s ecosystem delivers particularly significant challenges for attribution. Safari’s Intelligent Tracking Prevention caps first-party cookies at seven days. This creates recurring attribution decay: a user discovers your site through organic search on their iPhone, returns eight days later by typing the URL directly, but Safari has deleted the original tracking cookie. GA4 cannot recognize this returning visitor and classifies them as a brand new user arriving via “direct” traffic. The organic search that originally drove awareness receives zero credit for the return visit.
iOS 17’s Link Tracking Protection specifically targets advertising click IDs (gclid, fbclid) in links shared through Messages, Mail, and Safari Private Browsing. When users share paid ad links through these iOS channels, the click IDs that connect ad clicks to conversions get stripped away, breaking attribution even though UTM parameters may survive.
The Scale of Privacy Tool Adoption
Privacy tool adoption reaches levels that fundamentally impact analytics accuracy. Approximately 32% of American users block ads, according to Q1 2024 data from Global Web Index. Global adoption stands at 42.7% of users when accounting for all privacy tools including browser-native features.
Device usage patterns reveal concerning trends for marketers. Mobile devices show 48% ad blocker adoption, compared to 37% on desktop. While the percentage difference appears modest, mobile traffic now represents the majority of web sessions for most businesses – typically 60-70% of total traffic. This means mobile users generate 63% of all blocking activity despite only slightly higher adoption rates. Your mobile customers – often your most engaged, on-the-go audience – face the highest risk of attribution failure, and they represent the majority of your traffic.
| Region/Device Segment | Ad Blocker Adoption Rate | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| Global Average | 42.7% | All devices, 2024 |
| North America | 45% | All privacy tools included |
| United States | 32.2% | Ad blockers specifically |
| Mobile Devices | 48% | Higher than desktop |
| Desktop Computers | 37% | Browser extensions dominant |
The impact on data quality extends beyond simple ad blocking. GA4 underreports traffic by 11.2% on sites without consent banners, and this figure increases to 20.3% for sites that implement cookie consent requirements. Independent research estimates ad blockers reduce pageview reporting by 15-30%, with higher percentages for tech-savvy audiences.
The Business Cost of Misattribution
Consider a common scenario: your GA4 reports show that 40% of conversions originate from “direct” traffic, making it your top-performing channel. Meanwhile, organic search shows 25% and paid search shows 15%. Based on this data, you reduce your paid search budget. This decision feels data-driven and logical. However, it may rest on fundamentally flawed attribution.
Warning Signs: Organic Search Hiding in “Direct” Traffic
Red flags that organic search traffic is being systematically misattributed:
- Direct traffic to deep content pages: Users don’t type
yoursite.com/blog/complete-guide-to-marketing-attribution-2024– they discover these pages via search engines. - Declining organic + rising direct in equal amounts: If organic search sessions drop by 150 while direct rises by 150 in the same period, you witness attribution transfer, not channel performance change. Look for inverse correlation between these channels month-over-month.
- High mobile direct traffic: Safari’s 7-day cookie cap on iOS creates recurring organic search misattribution for return visitors who initially discovered your site through search.
- Direct traffic exhibiting search-like behavior: Multiple pages per session, longer engagement time, and high-intent keywords in site search suggest these users discovered you via search engines rather than typing your URL directly.
Bottom line: If your analytics show 35%+ direct traffic and you observe these patterns, organic search likely drives 50-70% more traffic than your reports indicate. Your SEO efforts perform far better than the data suggests.
The Strategic Danger of Undervaluing Organic Search
Marketing leaders cut budgets from seemingly underperforming channels, systematically defunding their most effective customer acquisition strategies. When organic search – often the highest-converting, highest-intent traffic – loses 60% of its attribution credit, businesses dramatically undervalue SEO investments.
Similarly, social media’s true impact remains hidden. SparkToro’s research reveals dark social’s massive impact. Private messaging platforms – WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, Slack, Discord – pass 0% attribution data. Every click appears as direct traffic. Even public social platforms show severe attribution failure: Instagram passes accurate attribution for only 30% of clicks, LinkedIn only 14%, and Pinterest only 12%. This means 70-88% of social traffic from these platforms gets misattributed.
The damage extends to automated systems. Google Ads and Facebook’s bidding algorithms require accurate conversion data. When conversions get misattributed to direct traffic, these algorithms receive incomplete signals. They may incorrectly conclude campaigns underperform, automatically reducing bids or narrowing targeting – creating a self-sabotaging feedback loop that compounds the attribution problem.
Calculating Your Hidden Revenue
Understanding Your Attribution Gap
Conservative Example Calculation:
Monthly Revenue: $500,000
Current “Direct” Traffic Share: 40%
Estimated Misattribution Within Direct: 30%
The Math:
$500,000 × 40% = $200,000 attributed to “Direct”
$200,000 × 30% = $60,000 likely originates from other sources
Breaking Down That $60,000 by True Source:
- ~$36,000 (60%): Likely originates from organic search
- ~$18,000 (30%): Likely originates from social media
- ~$6,000 (10%): Likely originates from paid ads, email, and referrals combined
This calculation suggests your organic search generates $36,000 more in monthly revenue than your analytics reports. Budget decisions that ignore this hidden performance systematically underfund your highest-intent acquisition channel.
Note: This example assumes revenue distributes proportionally to traffic share. Actual misattributed revenue may vary based on channel-specific conversion rates. However, organic search typically shows high conversion rates, meaning the real hidden value could exceed these conservative estimates.
The broader business implications prove severe. HubSpot research shows 76% of marketers struggle with multi-channel ROI attribution, while Gartner estimates businesses lose 20% of potential ROI due to incomplete or inaccurate tracking data.
Beyond budget misallocation, misattribution destroys visibility into the customer journey. Business owners lose the ability to answer critical questions: Which channels introduce new customers? Which channels assist conversions later in the sales cycle? When initial awareness-driving touchpoints – especially from organic search – disappear from the data, optimization efforts proceed with incomplete behavioral maps, fundamentally limiting growth potential.
Solutions to Improve Tracking Accuracy
While achieving perfect tracking accuracy remains impossible in today’s privacy-conscious landscape, businesses can implement strategies that significantly reduce misattribution and restore confidence in their data. This section organizes solutions by implementation effort and expected impact.
Tier 1: In-House Quick Wins (Implement This Week)
Before investing in complex solutions, audit your current setup and fix common issues. These improvements cost nothing but time and can reduce misattribution by 5-10%.
☐ Task 1: Audit Your UTM Tagging (30 minutes)
- Review your last 10 email campaigns – are all links consistently tagged?
- Check your social media posts – do URLs contain proper UTM parameters?
- Examine paid advertising landing pages for complete tagging
- Create a simple UTM template everyone on your team uses
- Tool: Use Google’s Campaign URL Builder (free)
Establishing consistent UTM tagging across all marketing links serves as the first line of defense. This includes links in email campaigns, social media posts, paid advertising, influencer partnerships, QR codes on print materials, and links in PDF documents. Even when ad blockers strip some parameters, maintaining rigorous tagging ensures maximum data capture for visitors without blocking tools.
☐ Task 2: Identify Deep-Page Direct Traffic (20 minutes)
- In GA4, create a segment: Direct traffic to non-homepage pages
- Check if “direct” visitors land on:
- Blog posts with long, complex URLs
- Product pages deep in your site hierarchy
- Downloadable resources or guides
- Any page users wouldn’t realistically type manually
- These patterns indicate organic search traffic being misattributed
☐ Task 3: Enable HTTPS Everywhere (varies by technical setup)
- Ensure your entire website operates on HTTPS to prevent referrer data loss
- Verify that internal links don’t mix HTTP and HTTPS protocols
- Mixed protocols break referrer data when users navigate from secure HTTPS pages to non-secure HTTP pages
Expected Impact: These foundational fixes can reduce misattribution by 5-10% and require no financial investment beyond staff time.
Tier 2: Strategic Improvements (Implement This Quarter)
Cross-Domain Tracking Configuration: Maintain consistent user identification when customer journeys span multiple domains, such as moving from a main website to a separate e-commerce platform. Without proper setup, each domain transition creates a new session classified as direct traffic.
Regular Redirect Audits: Confirm that 301 and 302 redirects preserve query strings, passing UTM parameters to final destinations. This ensures marketing attribution survives technical website changes like URL restructuring or content migrations.
First-Party Data Collection: Build first-party data collection through email lists, loyalty programs, and customer accounts. Customers who log in or provide email addresses create trackable identifiers that persist across sessions, providing tracking resilience against browser restrictions and ad blockers.
Tier 3: Advanced Solutions (Requires Technical Resources)
Server-Side Tracking Implementation: Server-side tracking represents a significant technical advancement for improving attribution accuracy, though it doesn’t provide a complete solution. Traditional client-side tracking relies on JavaScript code running in the user’s browser, sending data directly to Google’s servers – the exact process ad blockers target.
Server-side tracking shifts data collection to servers controlled by your business. Instead of browsers sending data directly to third parties, they send data to your own first-party domain (like analytics.yourcompany.com). Your server then processes and forwards this data to GA4 and other platforms. Because the initial request goes to a first-party domain, ad blockers using simple domain-based filter lists may be less likely to block it.
The results show meaningful improvement. Organizations implementing server-side tracking report recovering 10-15% more data. However, business owners should maintain realistic expectations. Server-side tracking does not completely bypass ad blockers, as more sophisticated blockers can still identify and block initial client-side requests based on recognizable JavaScript patterns or data payload structures.
Implementation Considerations:
- Requires server infrastructure and ongoing maintenance
- Costs typically range from $500-2,000+ monthly depending on traffic volume
- Needs technical expertise for correct implementation
- Must comply with GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy regulations
- Best suited for businesses with >100,000 monthly sessions or >$50,000 monthly ad spend
Analytical Approaches When Perfect Tracking Isn’t Possible
Marketing Mix Modeling: When user-level tracking proves insufficient, statistical models provide alternative measurement approaches. Marketing Mix Modeling measures marketing activity impact using historical aggregate data rather than individual user journeys, making it immune to client-side tracking issues.
MMM analyzes patterns in weekly ad spend per channel against total weekly sales, factoring in external variables like seasonality, economic trends, and competitive activity. This top-down approach provides strategic insights that complement user-level attribution data. Marketing Mix Modeling can statistically infer organic search’s true impact by analyzing correlations between search rankings, traffic patterns, and conversions – regardless of attribution accuracy.
Self-Reported Attribution: Post-purchase surveys provide qualitative insights that technology-based tracking cannot capture. Add “How did you hear about us?” fields to checkout flows, specifically including options for various channels: search engines, social media (specify platform), friend/family recommendation, podcast, blog post, or other sources. This approach uncovers the impact of word-of-mouth, podcasts, and other channels that prove technologically difficult to track.
Channel-Specific Remediation Strategies
For Organic Search (Your Most Vulnerable Channel):
- Segment direct traffic by landing page (15 minutes): Create GA4 custom segments that separate homepage direct traffic (potentially legitimate) from deep-page direct traffic (likely misattributed organic search).
- Monitor branded vs. non-branded patterns (20 minutes): Track site search queries from “direct” visitors. If they search for specific topics rather than navigating directly, they likely arrived via search engines.
- Use Google Search Console data (30 minutes monthly): Compare Search Console click data with GA4 organic search sessions. Large discrepancies indicate misattribution. Search Console provides server-side click data that ad blockers cannot affect.
- Implement Marketing Mix Modeling (requires specialist): MMM can statistically infer organic search’s true impact regardless of attribution accuracy.
For Social Media (High Dark Social Impact):
- Use dedicated share buttons (5 minutes per post): Implement social share buttons with pre-embedded UTM parameters rather than relying on native platform sharing.
- Deploy shortened URLs (~$30/month): Use branded link shorteners (Bitly, Rebrandly) with UTM parameters for all social posts. These services track clicks even when users copy-paste links into private messages.
- Survey customers (free): Add “How did you hear about us?” fields specifically including “Friend/Family recommendation” and “Social media” options to capture dark social impact.
For Paid Advertising (Moderate Protection Needed):
- Enable auto-tagging (5 minutes): Ensure Google Ads auto-tagging (gclid) and Facebook auto-advanced matching (fbclid) are active in platform settings.
- Layer manual UTMs (10 minutes per campaign): Add manual UTM parameters even when platforms auto-tag, providing redundancy if click IDs get stripped by iOS 17 Link Tracking Protection.
- Monitor platform vs. GA4 discrepancies (monthly, 30 minutes): Regular audits comparing Google Ads conversion reports with GA4 attribution reports can reveal gaps where conversions occurred but attribution failed.
Implementation Effort and Expected Impact
| Solution | Time Investment | Financial Cost | Data Improvement | Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTM Tagging Audit | 2-4 hours | $0 | 5-10% | In-house capable |
| HTTPS Implementation | 4-8 hours | $0-200 | 3-5% | In-house or developer |
| Cross-Domain Setup | 3-6 hours | $0 | 5-8% | In-house or developer |
| Link Shorteners | 1-2 hours setup | $30-100/month | 3-5% | In-house capable |
| Server-Side Tracking | 40-80 hours | $500-2K/month | 10-15% | Requires developer |
| Marketing Mix Model | 60-120 hours | $5K-50K | 15-25% | Requires specialist |
When to Handle In-House vs. Hiring Professional Help
You can likely handle internally:
- UTM tagging audits and standardization
- Basic GA4 configuration reviews
- Identifying direct traffic patterns and anomalies
- Simple cross-domain tracking setup
- Implementing social share buttons with UTM parameters
Consider professional expertise for:
- Server-side tracking implementation (requires development resources and ongoing maintenance)
- Marketing Mix Modeling (requires statistical expertise and historical data analysis)
- Large-scale tracking infrastructure for businesses with >$100K monthly ad spend
- GDPR/CCPA compliance consulting for international operations
- Custom attribution modeling and advanced analytics implementations
The complexity of modern tracking solutions – particularly server-side implementation – requires specialized expertise. These systems involve server infrastructure, data privacy compliance (GDPR, CCPA), ongoing maintenance, and technical troubleshooting. Professional implementation ensures proper configuration while avoiding costly mistakes that could compromise data quality or violate regulations.
More importantly, professionals can help interpret the disproportionate misattribution patterns specific to your business. Understanding that roughly 60% of your misattributed traffic likely originates from organic search allows for more accurate strategic planning, even without perfect tracking. Analytics specialists can implement sophisticated segmentation strategies, establish Marketing Mix Models, and create custom reporting that accounts for known attribution biases.
Getting Started: Your First Steps
Most businesses recover 10-15% of misattributed sessions through foundational improvements that require no consultants or complex implementations:
- Audit your current direct traffic percentage this week – If it exceeds 30%, investigate further using the Quick Audit checklist above
- Implement consistent UTM tagging across all marketing channels – Create a simple template everyone uses
- Segment your direct traffic – Separate legitimate direct visits (homepage, typed URLs) from likely misattributed search traffic (deep pages, long URLs)
These three steps cost nothing but time and provide clearer visibility into channel performance. Advanced solutions like server-side tracking or Marketing Mix Modeling can be evaluated once you’ve optimized the fundamentals.
Understanding Your Specific Attribution Gaps
The complexity of modern tracking solutions – particularly server-side implementation and Marketing Mix Modeling – requires specialized expertise. These systems involve server infrastructure, statistical analysis, data privacy compliance, and ongoing maintenance that extends beyond typical marketing team capabilities.
A professional analytics audit reveals your specific attribution gaps, quantifies the disproportionate impact on each marketing channel, and provides a realistic roadmap for improving data integrity tailored to your business size, technical resources, and budget constraints. Analytics specialists can implement sophisticated segmentation strategies, establish Marketing Mix Models, and create custom reporting that accounts for known attribution biases – allowing better strategic decisions even when perfect tracking remains impossible.
Taking Action on Attribution Challenges
Privacy tools and browser protections affect every business using digital analytics. With approximately 30% of “direct” traffic actually originating from other sources – and organic search representing roughly 60% of that misattributed traffic – understanding these patterns proves essential for accurate ROI measurement and strategic budget allocation.
The most damaging aspect extends beyond raw percentages of lost data. The disproportionate impact creates systematic undervaluation of your highest-performing channels. Your highest-intent, highest-converting traffic from organic search loses attribution credit at rates far exceeding email campaigns or branded search. This creates a dangerous illusion: analytics suggest direct brand recognition represents your top performer, when reality shows organic search and social media drive far more revenue than reports indicate.
The businesses that thrive in this privacy-first landscape proactively address attribution gaps rather than accepting them as inevitable. A multi-layered measurement approach combines technical improvements like server-side tracking with statistical modeling and qualitative insights, creating a robust framework that works within privacy constraints rather than fighting against them.
Key Takeaways
- Organic search loses approximately 60% of attribution credit – your SEO likely performs 50-70% better than reports suggest
- Social media misattribution ranges from 70-88% depending on platform, with private messaging passing 0% attribution
- Start with free quick wins: audit UTM tagging consistency, analyze direct traffic patterns for red flags, ensure HTTPS implementation across your entire site
- Server-side tracking improves accuracy by 10-15% but requires technical resources, ongoing maintenance, and realistic expectations about limitations
- Marketing Mix Modeling provides strategic insights when user-level tracking fails, using statistical analysis to infer true channel impact
- You cannot optimize campaigns you cannot accurately measure – and you cannot optimize when measurement systematically undervalues your best channels
The question facing businesses today extends beyond whether privacy tools affect analytics – they demonstrably do. The critical question becomes whether you adjust your strategy to account for the systematic underreporting of organic search and social media, or continue making significant budget decisions based on data you now understand contains fundamental distortions.
The competitive advantage belongs to businesses that understand organic search drives substantially more traffic than analytics reports, while competitors reduce SEO budgets based on incomplete data. As privacy regulations and browser protections continue evolving, successful measurement strategies will combine technical tracking improvements with statistical modeling and qualitative insights. No single approach provides perfect attribution, but a multi-layered strategy delivers the reliable data needed for confident marketing decisions.